- ... data1
- The general type float is the
most convenient one for general purpose library; In mathematical
morphology, a general type would rather be short, even if
PDE-based approaches are now in fashion.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ... tools2
- In future versions, C++ operator overloading
capabilities will be used in order to get a more natural way of
expressing formulas. For instance, minus(closing(f,B), f)
will be replaced by closing(f,B) - f!.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ...
border3
- In the case of the input image being a graph, since
the notion of border does not exist, calling
border::adapt_copy is still valid but does not execute any
code. Another approach is to set the border to
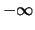 (
(
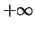 ) in the case of dilation (erosion).
) in the case of dilation (erosion).
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ... types4
- The queue-based priority
algorithm presented here is of course optimal for discrete data
types. However, the user can alsa call it when data are floating
values.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.