Difference between revisions of "Publications/xu.15.prl.inc"
From LRDE
Yongchao Xu (talk | contribs) |
Yongchao Xu (talk | contribs) |
||
| (39 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
=== Saliency Map Computation Relying on Mumford-Shah-Salient Level Line Selection === |
=== Saliency Map Computation Relying on Mumford-Shah-Salient Level Line Selection === |
||
| − | You can download the x86_64 binary to compute the saliency map representing hierarchical image simplification and segmentation [https://lrde.epita.fr/~xu/bin/saliency_map_mumford_ctos Here]. This application outputs the saliency map as a float image. The simplification and segmentation result can be obtained by thresholding this float image. Note that the image is twice as big |
+ | You can download the x86_64 binary to compute the saliency map representing hierarchical image simplification and segmentation [https://lrde.epita.fr/~xu/bin/saliency_map_mumford_ctos Here]. This application outputs the saliency map as a float image. The simplification and segmentation result can be obtained by thresholding this float image. Note that the image is twice as big as the original one and has a border for topogical and algorithmic purposes. Thus, any pixel with coordinates (x,y) in the original image is now at coordinates (2*(x+1), 2*(y+1)) in the saliency map. |
<pre> |
<pre> |
||
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
α₀ Grain filter size before merging trees (0 to disable) |
α₀ Grain filter size before merging trees (0 to disable) |
||
α₁ Grain filter size on the color ToS (0 to disable) |
α₁ Grain filter size on the color ToS (0 to disable) |
||
| + | </pre> |
||
| + | |||
| + | In the previous binary, we use the absolute difference between values |
||
| + | of neighboring pixels to compute the average of gradient's magnitude, |
||
| + | which is used to sort the shapes. An alternative is to use a gradient image given by a sophisticated |
||
| + | contour detection method (e.g., the |
||
| + | [http://research.microsoft.com/en-us/downloads/389109f6-b4e8-404c-84bf-239f7cbf4e3d Structured Edge]) |
||
| + | to compute the average of gradient's magnitude. You can |
||
| + | download this x86_64 binary [https://lrde.epita.fr/~xu/bin/saliency_map_mumford_ctos_grad Here]. |
||
| + | |||
| + | <pre> |
||
| + | Usage: ./saliency_map_mumford_ctos_grad input[rgb] α₀ α₁ gradSE.pgm output[float] |
||
| + | α₀ Grain filter size before merging trees (0 to disable) |
||
| + | α₁ Grain filter size on the color ToS (0 to disable) |
||
| + | gradSE Gradient image given by a contour detection method (Gpb or SE) |
||
</pre> |
</pre> |
||
<gallery> |
<gallery> |
||
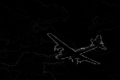
File:plane.jpg|Input RGB Image |
File:plane.jpg|Input RGB Image |
||
| − | File: |
+ | File:xu.15.prl-3063_map.png|Saliency map |
</gallery> |
</gallery> |
||
== Illustrations == |
== Illustrations == |
||
| + | === Saliency map computation on BSDS500 database === |
||
| − | === Natural image simplification with the Mumford-Shah functional optimized on the MToS === |
||
| + | |||
| − | The method minimizes the Mumford-Shah cartoon model constrained by the tree topology. It removes nodes from the tree until the energy doest not decrease anymore. |
||
| − | The |
+ | The first test was performed on the [http://www.eecs.berkeley.edu/Research/Projects/CS/vision/grouping/resources.html BSDS500] database. Some samples are given below and full results are available in this [https://lrde.epita.fr/~xu/material/saliency-maps-BSDS500.tar.gz archive]. The results are obtained |
| + | relying on the gradient image of Structured Edge. |
||
| + | |||
| + | <gallery caption="From top to bottom: input images; saliency maps; slight/moderate/strong simplification." perrow=5> |
||
| + | File:Xu.15.prl-100007.png |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| + | File:xu.15.prl-8068.png |
||
| + | File:xu.15.prl-189080.png |
||
| + | File:xu.15.prl-3096.png |
||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | File:Xu.15.prl-100007_map.png |
||
| + | File:xu.15.prl-196027_map.png |
||
| + | File:xu.15.prl-8068_map.png |
||
| + | File:xu.15.prl-189080_map.png |
||
| + | File:xu.15.prl-3096_map.png |
||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | File:Xu.15.prl-100007_less_simp.png |
||
| + | File:xu.15.prl-196027_less_simp.png |
||
| + | File:xu.15.prl-8068_less_simp.png |
||
| + | File:xu.15.prl-189080_less_simp.png |
||
| + | File:xu.15.prl-3096_less_simp.png |
||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | File:Xu.15.prl-100007_median_simp.png |
||
| + | File:xu.15.prl-196027_median_simp.png |
||
| + | File:xu.15.prl-8068_median_simp.png |
||
| + | File:xu.15.prl-189080_median_simp.png |
||
| + | File:xu.15.prl-3096_median_simp.png |
||
| + | |||
| + | File:Xu.15.prl-100007_strong_simp.png |
||
| + | File:xu.15.prl-196027_strong_simp.png |
||
| + | File:xu.15.prl-8068_strong_simp.png |
||
| + | File:xu.15.prl-189080_strong_simp.png |
||
| + | File:xu.15.prl-3096_strong_simp.png |
||
| + | |||
| + | </gallery> |
||
| + | |||
| + | === Saliency map computation on Weizmann database === |
||
| + | |||
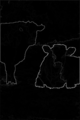
| + | The second test was performed on the [http://www.wisdom.weizmann.ac.il/~vision/Seg_Evaluation_DB/ Weizmann] database. Some samples are given below and full results are available in this [https://lrde.epita.fr/~xu/material/saliency-maps-weizmann-2obj.tar.gz archive]. The results are obtained relying on the gradient image of Structured Edge. |
||
| + | |||
| + | <gallery caption="From top to bottom: input images; saliency maps; slight/moderate/strong simplification." perrow=5> |
||
| + | File:Xu.15.prl-109300481333.png |
||
| + | File:xu.15.prl-112224059330.png |
||
| + | File:xu.15.prl-kata.png |
||
| + | File:xu.15.prl-hotblack_20070901_cows.png |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| + | |||
| + | File:Xu.15.prl-109300481333_map.png |
||
| + | File:xu.15.prl-112224059330_map.png |
||
| + | File:xu.15.prl-kata_beach_phuket_map.png |
||
| + | File:xu.15.prl-hotblack_20070901_cows_map.png |
||
| + | File:xu.15.prl-p5014757_cropped_map.png |
||
| + | File:Xu.15.prl-109300481333_less_simp.png |
||
| − | <gallery caption="Top: original images. Bottom: simplified images." perrow=5> |
||
| − | File: |
+ | File:xu.15.prl-112224059330_less_simp.png |
| − | File: |
+ | File:xu.15.prl-kata_beach_phuket_less_simp.png |
| + | File:xu.15.prl-hotblack_20070901_cows_less_simp.png |
||
| − | File:carlinet.15.tip-B17paul1444.png |
||
| + | File:xu.15.prl-p5014757_cropped_less_simp.png |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| − | File: |
+ | File:Xu.15.prl-109300481333_median_simp.png |
| − | File: |
+ | File:xu.15.prl-112224059330_median_simp.png |
| − | File: |
+ | File:xu.15.prl-kata_beach_phuket_median_simp.png |
| + | File:xu.15.prl-hotblack_20070901_cows_median_simp.png |
||
| − | File:carlinet.15.tip-nopeeking_simp.png |
||
| + | File:xu.15.prl-p5014757_cropped_median_simp.png |
||
| − | File:P5014757_cropped.png |
||
| + | File:Xu.15.prl-109300481333_strong_simp.png |
||
| + | File:xu.15.prl-112224059330_strong_simp.png |
||
| + | File:xu.15.prl-kata_beach_phuket_strong_simp.png |
||
| + | File:xu.15.prl-hotblack_20070901_cows_strong_simp.png |
||
| + | File:xu.15.prl-p5014757_cropped_strong_simp.png |
||
</gallery> |
</gallery> |
||
Latest revision as of 12:38, 10 March 2016
Materials
Mumford-Shah Simplification on the Color Tree of Shapes
You can download the x86_64 binary to compute the Mumford-Shah simplification running on the color tree of shapes Here.
Usage: ./mumford_shah_on_ctos input[rgb] α₀ α₁ λ output[rgb] α₀ Grain filter size before merging trees (0 to disable) α₁ Grain filter size on the color ToS (0 to disable) λ Mumford-shah regularisation weight (e.g. 5000)
Saliency Map Computation Relying on Mumford-Shah-Salient Level Line Selection
You can download the x86_64 binary to compute the saliency map representing hierarchical image simplification and segmentation Here. This application outputs the saliency map as a float image. The simplification and segmentation result can be obtained by thresholding this float image. Note that the image is twice as big as the original one and has a border for topogical and algorithmic purposes. Thus, any pixel with coordinates (x,y) in the original image is now at coordinates (2*(x+1), 2*(y+1)) in the saliency map.
Usage: ./saliency_map_mumford_ctos input[rgb] α₀ α₁ output[float] α₀ Grain filter size before merging trees (0 to disable) α₁ Grain filter size on the color ToS (0 to disable)
In the previous binary, we use the absolute difference between values of neighboring pixels to compute the average of gradient's magnitude, which is used to sort the shapes. An alternative is to use a gradient image given by a sophisticated contour detection method (e.g., the Structured Edge) to compute the average of gradient's magnitude. You can download this x86_64 binary Here.
Usage: ./saliency_map_mumford_ctos_grad input[rgb] α₀ α₁ gradSE.pgm output[float] α₀ Grain filter size before merging trees (0 to disable) α₁ Grain filter size on the color ToS (0 to disable) gradSE Gradient image given by a contour detection method (Gpb or SE)
Illustrations
Saliency map computation on BSDS500 database
The first test was performed on the BSDS500 database. Some samples are given below and full results are available in this archive. The results are obtained relying on the gradient image of Structured Edge.
- From top to bottom: input images; saliency maps; slight/moderate/strong simplification.
Saliency map computation on Weizmann database
The second test was performed on the Weizmann database. Some samples are given below and full results are available in this archive. The results are obtained relying on the gradient image of Structured Edge.
- From top to bottom: input images; saliency maps; slight/moderate/strong simplification.